Click on prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes to reveal a list of word parts to memorize for the Digestive System.
The digestive system is continually at work, yet people seldom appreciate the complex tasks it performs in a choreographed biologic symphony. Consider what happens when you eat an apple. Of course, you enjoy the apple’s taste as you chew it, but in the hours that follow, unless something goes amiss and you get a stomachache, you don’t notice that your digestive system is working. You may be taking a walk or studying or sleeping, having forgotten all about the apple, but your stomach and intestines are busy digesting it and absorbing its vitamins and other nutrients. By the time any waste material is excreted, the body has appropriated all it can use from the apple. In short, whether you pay attention or not, the organs of the digestive system perform their specific functions, allowing you to use the food you eat to keep you going.
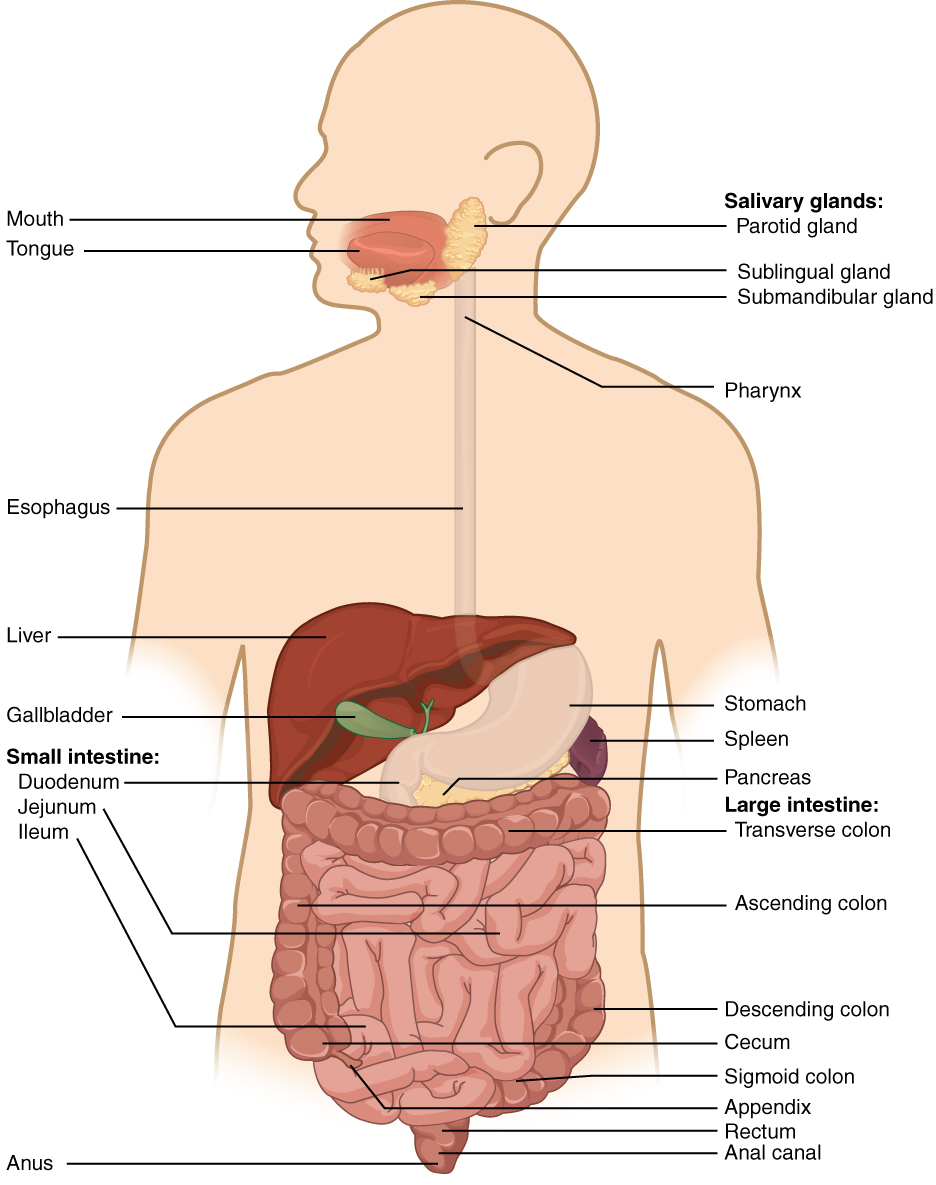
This chapter examines the structure and functions of these organs and explores the mechanics and chemistry of the digestive processes. The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although the small intestine is the workhorse of the system, where the majority of digestion occurs, and where most of the released nutrients are absorbed into the blood or lymph, each of the digestive system organs makes a vital contribution to this process (see Figure 13.1).

The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). The structures of the mouth are illustrated in Figure 13.2.
At the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). Their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper. Lips are very vascular with a thin layer of keratin; hence, the reason they are red.
The pocket-like part of the mouth that is framed on the inside by the gums and teeth, and on the outside by the cheeks and lips is called the oral vestibule. Moving farther into the mouth, the opening between the oral cavity and throat (oropharynx) is called the fauces (like the kitchen “faucet”). The main open area of the mouth, or oral cavity proper, runs from the gums and teeth to the fauces.
When you are chewing, you do not find it difficult to breathe simultaneously. The next time you have food in your mouth, notice how the arched shape of the roof of your mouth allows you to handle both digestion and respiration at the same time. This arch is called the palate. The anterior region of the palate serves as a wall (or septum) between the oral and nasal cavities as well as a rigid shelf against which the tongue can push food. It is created by the maxillary and palatine bones of the skull and, given its bony structure, is known as the hard palate. If you run your tongue along the roof of your mouth, you’ll notice that the hard palate ends in the posterior oral cavity, and the tissue becomes fleshier. This part of the palate, known as the soft palate, is composed mainly of skeletal muscle. You can therefore manipulate, subconsciously, the soft palate—for instance, to yawn, swallow, or sing (see Figure 13.2).
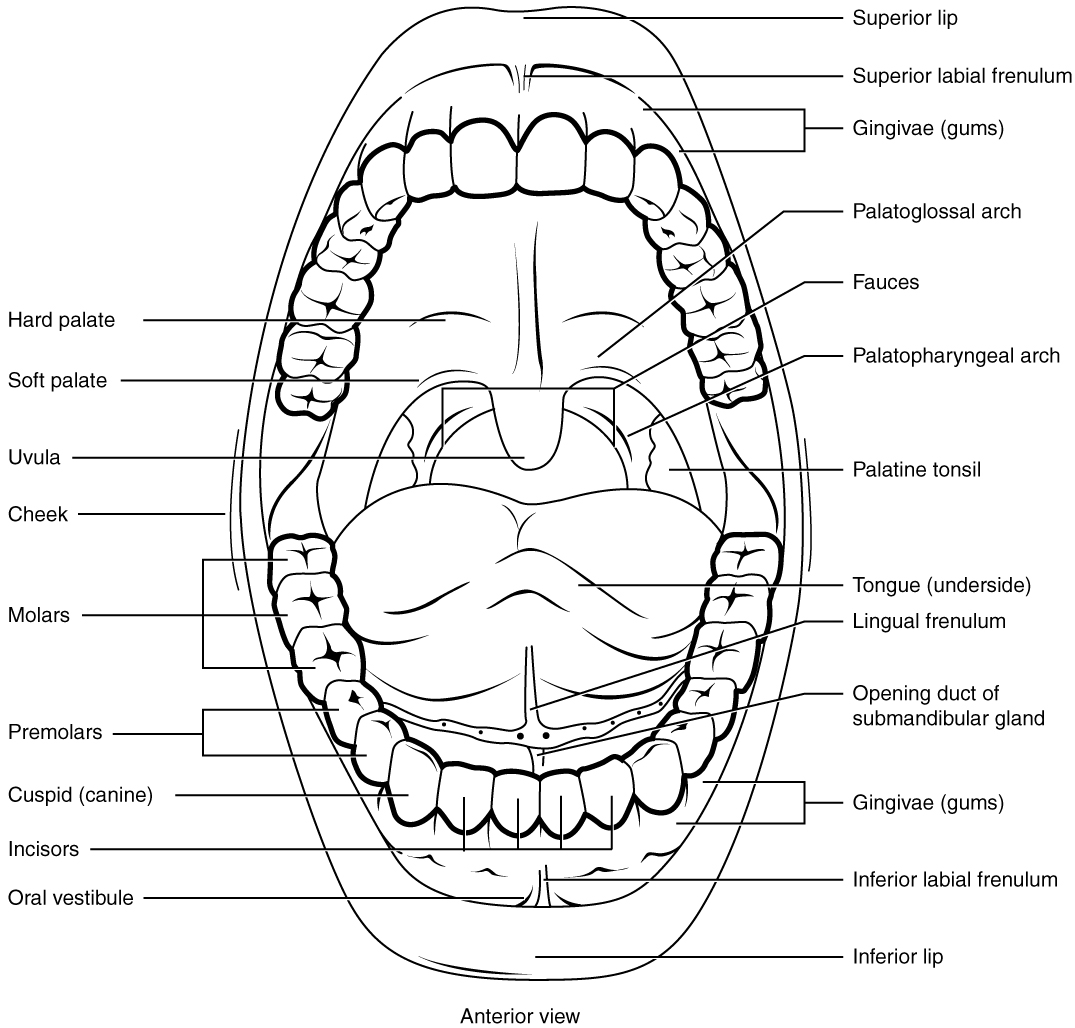
A fleshy bead of tissue called the uvula drops down from the center of the posterior edge of the soft palate. Although some have suggested that the uvula is a vestigial organ, it serves an important purpose. When you swallow, the soft palate and uvula move upward, helping to keep foods and liquid from entering the nasal cavity. Unfortunately, it can also contribute to the sound produced by snoring. Two muscular folds extend downward from the soft palate, on either side of the uvula. Toward the front, the palatoglossal arch lies next to the base of the tongue; behind it, the palatopharyngeal arch forms the superior and lateral margins of the fauces. Between these two arches are the palatine tonsils, clusters of lymphoid tissue that protect the pharynx. The lingual tonsils are located at the base of the tongue.
You can eat upside down. Food doesn’t need gravity to reach your stomach. Peristalsis, a wave-like muscle movement, pushes food along.
Perhaps you have heard it said that the tongue is the strongest muscle in the body. Those who stake this claim cite its strength proportional to its size. Although it is difficult to quantify the relative strength of different muscles, it remains indisputable that the tongue is a workhorse, facilitating ingestion, mechanical digestion, chemical digestion (lingual lipase), sensation (of taste, texture, and temperature of food), swallowing, and vocalization.
The tongue is attached to the mandible, the styloid processes of the temporal bones, and the hyoid bone. The hyoid is unique in that it only distantly/indirectly articulates with other bones. The tongue is positioned over the floor of the oral cavity. A medial septum extends the entire length of the tongue, dividing it into symmetrical halves.
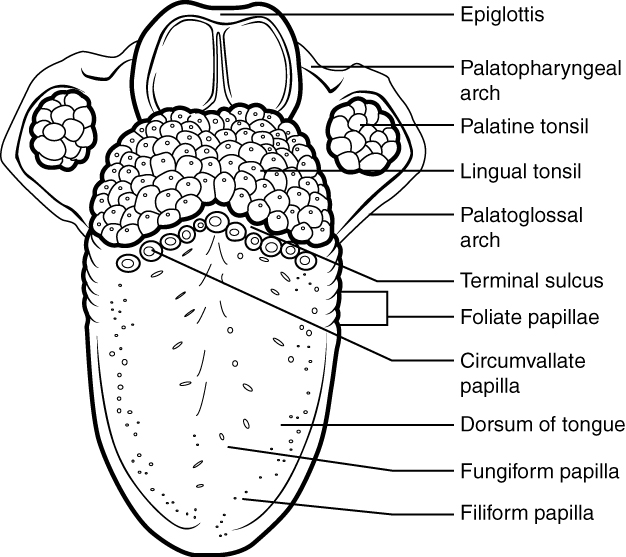
The top and sides of the tongue are studded with papillae, extensions of lamina propria of the mucosa, which are covered in stratified squamous epithelium (see Figure 13.3).
Many small salivary glands are housed within the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue. These minor exocrine glands are constantly secreting saliva, either directly into the oral cavity or indirectly through ducts, even while you sleep. In fact, an average of 1 to 1.5 liters of saliva is secreted each day. Usually, just enough saliva is present to moisten the mouth and teeth. Secretion increases when you eat because saliva is essential to moisten food and initiate the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates. Small amounts of saliva are also secreted by the labial glands in the lips. In addition, the buccal glands in the cheeks, palatal glands in the palate, and lingual glands in the tongue help ensure that all areas of the mouth are supplied with adequate saliva.
The pharynx (throat) is involved in both digestion and respiration. It receives food and air from the mouth, and air from the nasal cavities. When food enters the pharynx, involuntary muscle contractions close off the air passageways. A short tube of skeletal muscle lined with a mucous membrane, the pharynx runs from the posterior oral and nasal cavities to the opening of the esophagus and larynx. It has three subdivisions. The most superior, the nasopharynx, is involved only in breathing and speech. The other two subdivisions, the oropharynx and the laryngopharynx, are used for both breathing and digestion. The oropharynx begins inferior to the nasopharynx and is continuous below with the laryngopharynx. The inferior border of the laryngopharynx connects to the esophagus, whereas the anterior portion connects to the larynx, allowing air to flow into the bronchial tree.
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach. It is approximately 25.4 cm (10 in) in length, located posterior to the trachea, and remains in a collapsed form when not engaged in swallowing. As you can see in Figure 13.4, the esophagus runs a mainly straight route through the mediastinum of the thorax. To enter the abdomen, the esophagus penetrates the diaphragm through an opening called the esophageal hiatus.
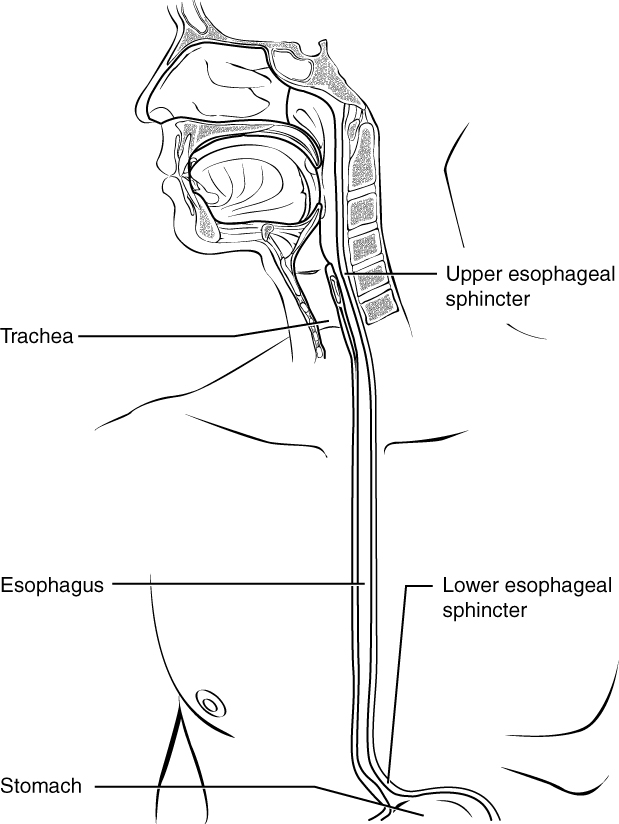
The upper esophageal sphincter, which is continuous with the inferior pharyngeal constrictor, controls the movement of food from the pharynx into the esophagus. The upper two-thirds of the esophagus consists of both smooth and skeletal muscle fibers, with the latter fading out in the bottom third of the esophagus. Rhythmic waves of peristalsis, which begin in the upper esophagus, propel the bolus of food toward the stomach. Meanwhile, secretions from the esophageal mucosa lubricate the esophagus and food. Food passes from the esophagus into the stomach at the lower esophageal sphincter (also called the gastroesophageal or cardiac sphincter). Recall that sphincters are muscles that surround tubes and serve as valves, closing the tube when the sphincters contract and opening it when they relax.
There are four main regions in the stomach: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus (see Figure 13.5). The cardia (or cardiac region) is the point where the esophagus connects to the stomach and through which food passes into the stomach. Located inferior to the diaphragm, above and to the left of the cardia, is the dome-shaped fundus. Below the fundus is the body, the main part of the stomach. The funnel-shaped pylorus connects the stomach to the duodenum. The wider end of the funnel, the pyloric antrum, connects to the body of the stomach. The narrower end is called the pyloric canal, which connects to the duodenum. The smooth muscle pyloric sphincter is located at this latter point of connection and controls stomach emptying. In the absence of food, the stomach deflates inward, and its mucosa and submucosa fall into a large fold called a ruga.
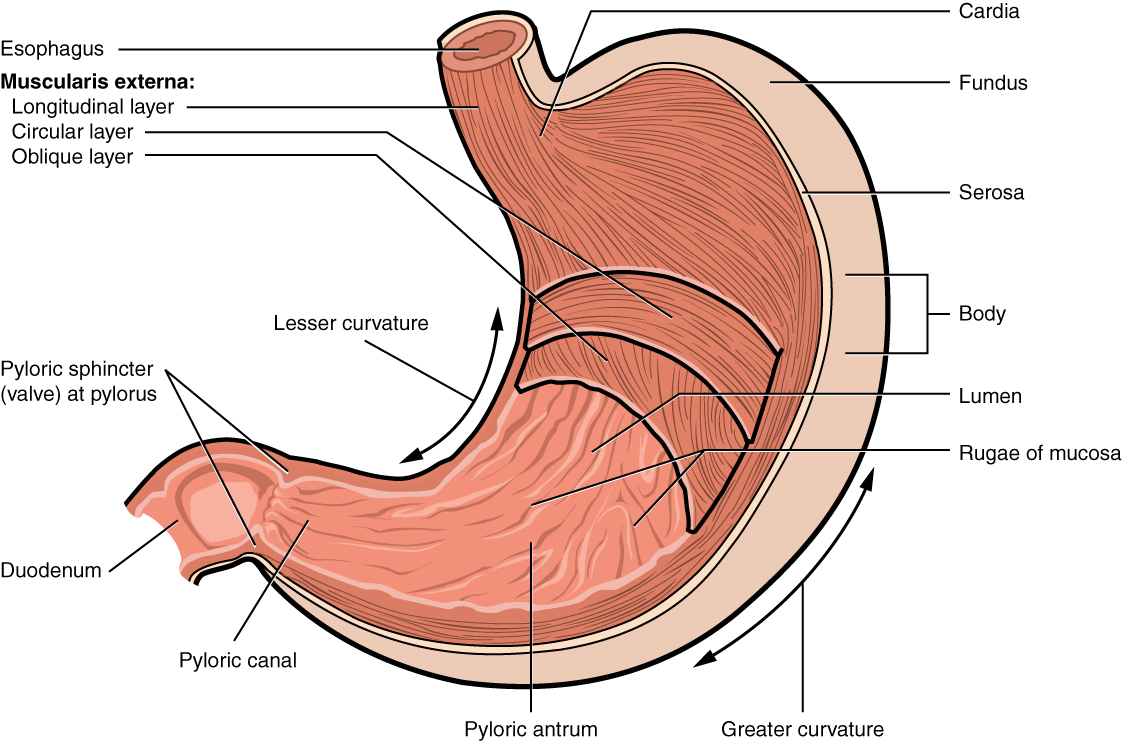
The convex lateral surface of the stomach is called the greater curvature; the concave medial border is the lesser curvature. The stomach is held in place by the lesser omentum, which extends from the liver to the lesser curvature, and the greater omentum, which runs from the greater curvature to the posterior abdominal wall.
Chyme released from the stomach enters the small intestine, which is the primary digestive organ in the body. Not only is this where most digestion occurs, but it is also where practically all absorption occurs. The longest part of the alimentary canal, the small intestine, is about 3.05 meters (10 feet) long in a living person (but about twice as long in a cadaver due to the loss of muscle tone). Since this makes it about five times longer than the large intestine, you might wonder why it is called “small.” In fact, its name derives from its relatively smaller diameter of only about 2.54 cm (1 in), compared with 7.62 cm (3 in) for the large intestine. As you will see shortly, in addition to its length, the folds and projections of the lining of the small intestine work to give it an enormous surface area, which is approximately 200 m 2 , more than 100 times the surface area of your skin. This large surface area is necessary for complex processes of digestion and absorption that occur within it.
The coiled tube of the small intestine is subdivided into three regions. From proximal to distal, these are the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum (see Figure 13.6).
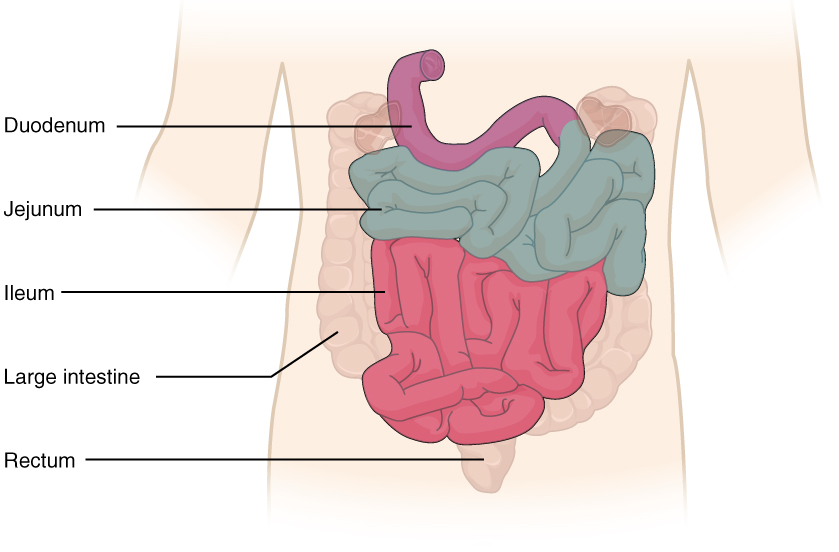
Your body absorbs 90% of your nutrients through the small intestine into your blood.
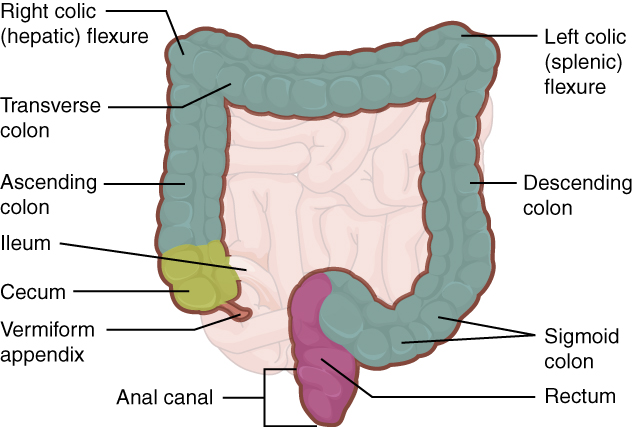
The large intestine is the terminal part of the alimentary canal. The primary function of this organ is to finish absorption of nutrients and water, synthesize certain vitamins, form feces, and eliminate feces from the body. The large intestine runs from the appendix to the anus. It frames the small intestine on three sides. Despite its being about one-half as long as the small intestine, it is called large because it is more than twice the diameter of the small intestine, about 3 inches. The large intestine is subdivided into four main regions: the cecum, the colon, the rectum, and the anus. The ileocecal valve, located at the opening between the ileum and the large intestine, controls the flow of chyme from the small intestine to the large intestine.
The first part of the large intestine is the cecum, a sac-like structure that is suspended inferior to the ileocecal valve. It is about 6 cm (2.4 in) long, receives the contents of the ileum, and continues the absorption of water and salts. The appendix (or vermiform appendix) is a winding tube that attaches to the cecum. Although the 7.6-cm (3-in) long appendix contains lymphoid tissue, suggesting an immunologic function, this organ is generally considered vestigial. However, at least one recent report assumes a survival advantage conferred by the appendix: in diarrheal illness, the appendix may serve as a bacterial reservoir to repopulate the enteric bacteria for those surviving the initial phases of the illness. Moreover, its twisted anatomy provides a haven for the accumulation and multiplication of enteric bacteria. The mesoappendix, the mesentery of the appendix, tethers it to the mesentery of the ileum.
The cecum blends seamlessly with the colon. Upon entering the colon, the food residue first travels up the ascending colon on the right side of the abdomen. At the inferior surface of the liver, the colon bends to form the right colic flexure (hepatic flexure) and becomes the transverse colon. The region defined as the hindgut begins with the last third of the transverse colon and continues. Food residue passing through the transverse colon travels across to the left side of the abdomen, where the colon angles sharply immediately inferior to the spleen, at the left colic flexure (splenic flexure). From there, food residue passes through the descending colon, which runs down the left side of the posterior abdominal wall. After entering the pelvis inferiorly, it becomes the s-shaped sigmoid colon, which extends medially to the midline (see Figure 13.7). The ascending and descending colon, and the rectum (discussed next) are located in the retroperitoneum. The transverse and sigmoid colon are tethered to the posterior abdominal wall by the mesocolon.
Chemical digestion in the small intestine relies on the activities of three accessory digestive organs: the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder (see Figure 13.8). The digestive role of the liver is to produce bile and export it to the duodenum. The gallbladder primarily stores, concentrates, and releases bile. The pancreas produces pancreatic juice, which contains digestive enzymes and bicarbonate ions, and delivers it to the duodenum.
On the Figure 13.8 diagram, locate the following anatomical organs and consider how these organs support the digestive process
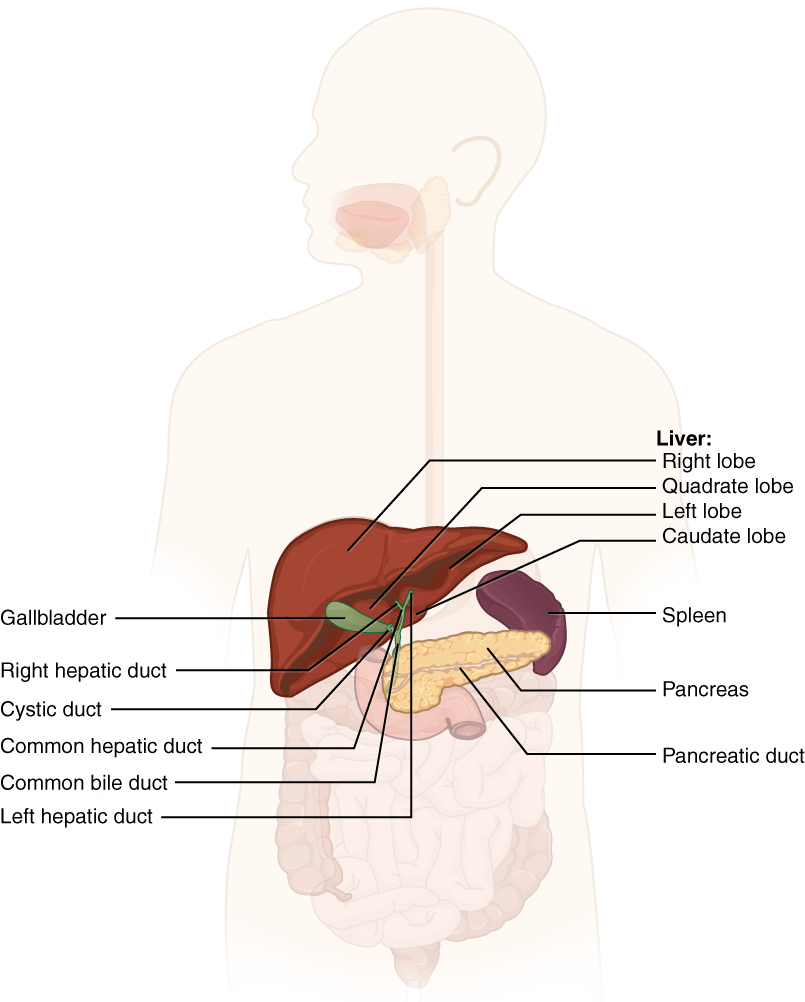
The liver is the largest gland in the body, weighing about three pounds in an adult. It is also one of the most important organs. In addition to being an accessory digestive organ, it plays a number of roles in metabolism and regulation. The liver lies inferior to the diaphragm in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity and receives protection from the surrounding ribs.
The liver is divided into two primary lobes: a large right lobe and a much smaller left lobe. In the right lobe, some anatomists also identify an inferior quadrate lobe and a posterior caudate lobe, which are defined by internal features. The liver is connected to the abdominal wall and diaphragm by five peritoneal folds referred to as ligaments.
The porta hepatis (“gate to the liver”) is where the hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein enter the liver. These two vessels, along with the common hepatic duct, run behind the lateral border of the lesser omentum on the way to their destinations. The hepatic portal vein delivers partially deoxygenated blood containing nutrients absorbed from the small intestine and actually supplies more oxygen to the liver than do the much smaller hepatic arteries. In addition to nutrients, drugs and toxins are also absorbed. After processing the bloodborne nutrients and toxins, the liver releases nutrients needed by other cells back into the blood, which drains into the central vein and then through the hepatic vein to the inferior vena cava. With this hepatic portal circulation, all blood from the alimentary canal passes through the liver. This largely explains why the liver is the most common site for the metastasis of cancers that originate in the alimentary canal.
Bile produced by the liver is a mixture secreted by the liver to accomplish the emulsification of lipids in the small intestine.
Bilirubin, the main bile pigment, is a waste product produced when the spleen removes old or damaged red blood cells from the circulation. These breakdown products, including proteins, iron, and toxic bilirubin, are transported to the liver via the splenic vein of the hepatic portal system. In the liver, proteins and iron are recycled, whereas bilirubin is excreted in the bile. It accounts for the green color of bile. Bilirubin is eventually transformed by intestinal bacteria into stercobilin, a brown pigment that gives your stool its characteristic color. In some disease states, bile does not enter the intestine, resulting in white (‘acholic’) stool with a high fat content, since virtually no fats are broken down or absorbed.
Between meals, bile is produced but conserved. The valve-like hepatopancreatic ampulla closes, allowing bile to divert to the gallbladder, where it is concentrated and stored until the next meal.
The soft, oblong, glandular pancreas lies transversely in the retroperitoneum behind the stomach. Its head is nestled into the “c-shaped” curvature of the duodenum with the body extending to the left about 15.2 cm (6 in) and ending as a tapering tail in the hilum of the spleen. It is a curious mix of exocrine (secreting digestive enzymes) and endocrine (releasing hormones into the blood) functions (Figure 13.9).
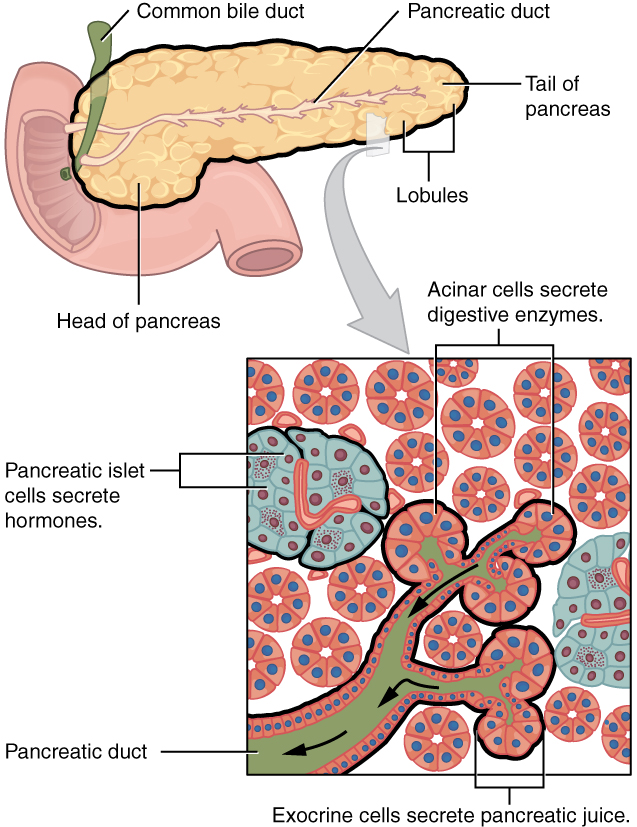
The exocrine part of the pancreas arises as little grape-like cell clusters, each called an acinus (plural = acini), located at the terminal ends of pancreatic ducts. These acinar cells secrete enzyme-rich pancreatic juice into tiny merging ducts that form two dominant ducts. The larger duct fuses with the common bile duct (carrying bile from the liver and gallbladder) just before entering the duodenum via a common opening (the hepatopancreatic ampulla). The smooth muscle sphincter of the hepatopancreatic ampulla controls the release of pancreatic juice and bile into the small intestine. The second and smaller pancreatic duct, the accessory duct (duct of Santorini), runs from the pancreas directly into the duodenum, approximately 1 inch above the hepatopancreatic ampulla. When present, it is a persistent remnant of pancreatic development.
Scattered through the sea of exocrine acini are small islands of endocrine cells, the islets of Langerhans. These vital cells produce the hormones pancreatic polypeptide, insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin.
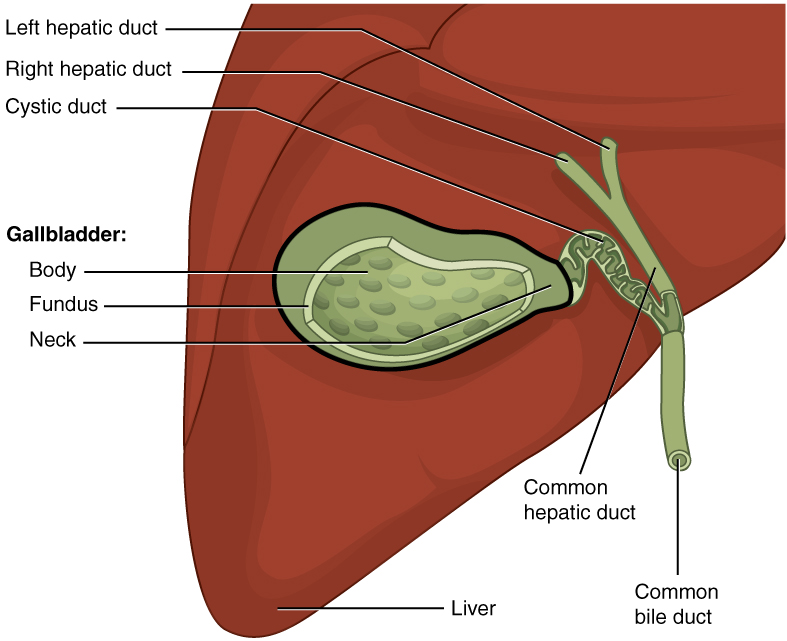
The gallbladder is 8 to 10 cm (~3 to 4 in) long and is nested in a shallow area on the posterior aspect of the right lobe of the liver. This muscular sac stores, concentrates, and, when stimulated, propels the bile into the duodenum via the common bile duct. It is divided into three regions. The fundus is the widest portion and tapers medially into the body, which in turn narrows to become the neck. The neck angles slightly superiorly as it approaches the hepatic duct. The cystic duct is 1 to 2 cm (less than 1 in) long and turns inferiorly as it bridges the neck and hepatic duct.
The simple columnar epithelium of the gallbladder mucosa is organized in rugae, similar to those of the stomach. There is no submucosa in the gallbladder wall. The wall’s middle, muscular coat is made of smooth muscle fibers. When these fibers contract, the gallbladder’s contents are ejected through the cystic duct and into the bile duct (Figure 13.10). The visceral peritoneum reflected from the liver capsule holds the gallbladder against the liver and forms the outer coat of the gallbladder. The gallbladder’s mucosa absorbs water and ions from bile, concentrating it by up to 10-fold.
At rest, about 1500 mL of blood per minute flows through the liver. What percentage of this blood flow comes from the hepatic portal system?
The main functions of the digestive system are:
The processes of digestion include six activities: ingestion, propulsion, mechanical or physical digestion, chemical digestion, absorption, and defecation.
The first of these processes, ingestion, refers to the entry of food into the alimentary canal through the mouth. There, the food is chewed and mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that begin breaking down the carbohydrates in the food plus some lipid digestion via lingual lipase. Chewing increases the surface area of the food and allows an appropriately sized bolus to be produced.
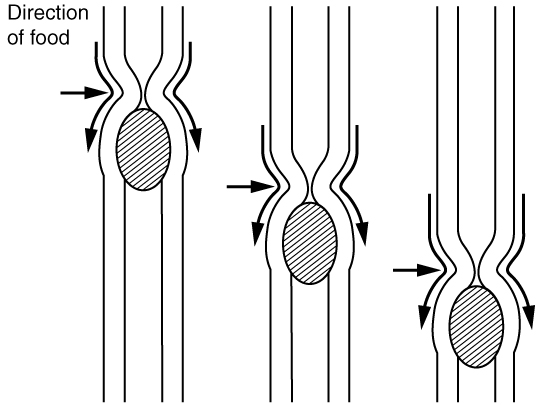
Food leaves the mouth when the tongue and pharyngeal muscles propel it into the esophagus. This act of swallowing, the last voluntary act until defecation, is an example of propulsion, which refers to the movement of food through the digestive tract. It includes both the voluntary process of swallowing and the involuntary process of peristalsis. Peristalsis consists of sequential, alternating waves of contraction and relaxation of alimentary wall smooth muscles, which act to propel food along (see Figure 13.11). These waves also play a role in mixing food with digestive juices. Peristalsis is so powerful that foods and liquids you swallow enter your stomach even if you are standing on your head.
Digestion includes both mechanical and chemical processes. Mechanical digestion is a purely physical process that does not change the chemical nature of the food. Instead, it makes the food smaller to increase both surface area and mobility. It includes mastication, or chewing, as well as tongue movements that help break food into smaller bits and mix food with saliva. Although there may be a tendency to think that mechanical digestion is limited to the first steps of the digestive process, it occurs after the food leaves the mouth, as well. The mechanical churning of food in the stomach serves to further break it apart and expose more of its surface area to digestive juices, creating an acidic “soup” called chyme.
Segmentation, which occurs mainly in the small intestine, consists of localized contractions of circular muscle of the muscularis layer of the alimentary canal. These contractions isolate small sections of the intestine, moving their contents back and forth while continuously subdividing, breaking up, and mixing the contents. By moving food back and forth in the intestinal lumen, segmentation mixes food with digestive juices and facilitates absorption.
In chemical digestion, starting in the mouth, digestive secretions break down complex food molecules into their chemical building blocks (for example, proteins into separate amino acids). These secretions vary in composition but typically contain water, various enzymes, acids, and salts. The process is completed in the small intestine.
Food that has been broken down is of no value to the body unless it enters the bloodstream and its nutrients are put to work. This occurs through the process of absorption, which takes place primarily within the small intestine. There, most nutrients are absorbed from the lumen of the alimentary canal into the bloodstream through the epithelial cells that make up the mucosa. Lipids are absorbed into lacteals and are transported via the lymphatic vessels to the bloodstream.
In defecation, the final step in digestion, undigested materials are removed from the body as feces.
Age-related changes in the digestive system begin in the mouth and can affect virtually every aspect of the digestive system. Taste buds become less sensitive, so food isn’t as appetizing as it once was. A slice of pizza is a challenge, not a treat, when you have lost teeth, your gums are diseased, and your salivary glands aren’t producing enough saliva. Swallowing can be difficult, and ingested food moves slowly through the alimentary canal because of reduced strength and tone of muscular tissue. Neurosensory feedback is also dampened, slowing the transmission of messages that stimulate the release of enzymes and hormones.
Pathologies that affect the digestive organs—such as hiatal hernia, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease—can occur at greater frequencies as you age. Problems in the small intestine may include duodenal ulcers, maldigestion, and malabsorption. Problems in the large intestine include hemorrhoids, diverticular disease, and constipation. Conditions that affect the function of accessory organs—and their abilities to deliver pancreatic enzymes and bile to the small intestine—include jaundice, acute pancreatitis, cirrhosis, and gallstones.
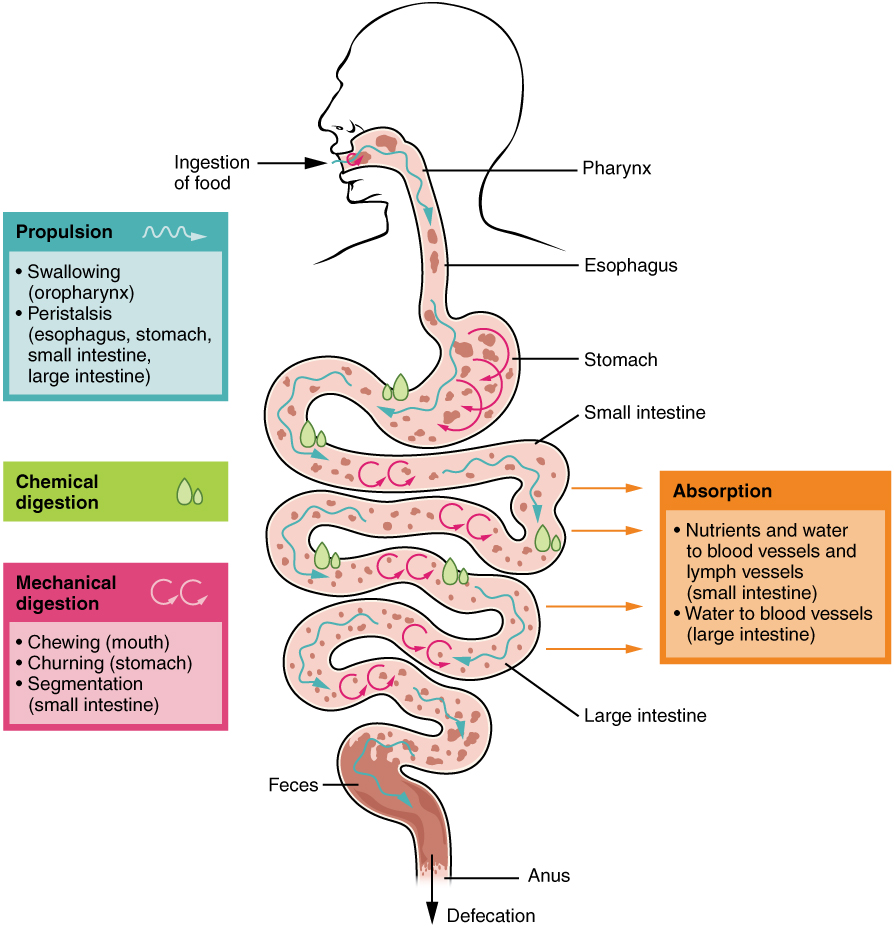
In some cases, a single organ is in charge of a digestive process. For example, ingestion occurs only in the mouth and defecation only in the anus. However, most digestive processes involve the interaction of several organs and occur gradually as food moves through the alimentary canal (see Figure 13.12). Some chemical digestion occurs in the mouth. Some absorption can occur in the mouth and stomach; for example, alcohol and aspirin.
Neural and endocrine regulatory mechanisms work to maintain the optimal conditions in the lumen needed for digestion and absorption. These regulatory mechanisms, which stimulate digestive activity through mechanical and chemical activity, are controlled both extrinsically and intrinsically.
Many terms and phrases related to the digestive system are abbreviated. Learn these common abbreviations by expanding the list below.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is caused by stomach acid flowing upwards into the esophagus. Those suffering from the condition will often feel a burning sensation in the chest or throat (MedlinePlus, 2021a). To learn more about GERD, visit the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases’ web page.
Cholecystitis is known as inflammation of the gallbladder. Gall stone development can block the gallbladder’s release of bile, leading to an inflammatory response. Cholecystitis can be characterized as acute (the sudden onset of irritation of the gallbladder) or chronic (prolonged irritation of the gallbladder usually caused by repeated bouts of acute cholecystitis). Treatment may require a cholecystectomy (Jones, Genova, et al., 2021; Jones, Gnanapandithan, et al., 2021). To learn more, visit the Mayo Clinic’s web page on cholecystitis.
Cirrhosis is a condition whereby the liver scars. Potentially fatal complications can arise, including liver failure. It generally cannot be reversed, although many of the underlying causes of cirrhosis can be treated and may help lower the likelihood of cirrhosis-related complications. Cirrhosis is caused by different forms of liver disease and chronic alcoholism (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, n.d.-a).
Cirrhosis often has no signs or symptoms until liver damage is extensive and may include:
Esophageal cancer begins in the innermost layer of the esophagus and spreads to the other layers. Risk factors include tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and older age (National Cancer Institute, 2021a). To learn more, visit the Mayo Clinic’s web page on esophageal cancer.
Inflammation of the liver is referred to as hepatitis. It can be caused by heavy alcohol use, toxins, drugs, or as a result of an autoimmune response, but it is most often caused by a virus. Viral hepatitis is caused by one of several viruses: hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E. In the United States, 90% of hepatitis cases are caused by the A, B, and C viruses. Many cases are asymptomatic (Mehta & Reddivari, 2021).
Individuals who possess celiac disease have an immune sensitivity reaction occurring in the small intestines when they consume gluten. Typically people with this condition are genetically predisposed to the condition. Damage to the small intestine will occur if continued consumption of gluten occurs. Following a gluten-free diet generally resolves most symptoms and complications of celiac disease (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, n.d.-b). For more information, visit the Mayo Clinic’s web page on celiac disease.
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) whereby a section or segments of the digestive tract experience inflammation. Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere along the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus, although it is most often found in the small intestines. This often leads to the malabsorption of nutrients from food. Ulcerative colitis is localized inflammation and ulcers in the colon (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, n.d.-c, n.d.-d). To learn more, visit the Mayo Clinic’s web pages on Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Colon cancer is cancer formation in the colon portion of the digestive tract. Familial or personal history of rectal or colon cancer, heavy use of tobacco or alcohol, and older age are risk factors for colon cancer. It is often diagnosed through a colonoscopy (National Cancer Institute, 2021b). To learn more, visit the National Cancer Institute’s web page on colon cancer.
A hernia occurs when part of an organ or tissue squeezes through a weak spot in a surrounding muscle. A hernia can happen in the groin (inguinal hernia), around the belly button (umbilical hernia), through a scar (incisional hernia), through the diaphragm (hiatal hernia), or as a result of a birth defect (congenital diaphragmatic hernia) (MedlinePlus, 2021b). For more information, visit the Cleveland Clinic’s web page on hernias.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common disorder affecting the large intestines. It often involves abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel movements, although individuals with IBS may experience remission and flare-ups. Diet and lifestyle modifications often help in the management of the condition. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, n.d.-e). To learn more, visit the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases’ web page on IBS.
A polyp is a small growth of tissue protruding from the intestinal wall. Most are harmless but can transition over time into a cancerous growth. Typically, they are found in men and adults. over the age of 45 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, n.d.-f). To learn more, review the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases’ web page on polyps.
Gastroenterology is a branch of internal medicine that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of conditions afflicting the digestive system. A physician who specializes in this area is known as a gastroenterologist. (Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021; National Cancer Institute, n.d.). To learn more about gastroenterology, visit the American College of Gastroenterology’s web page.
Upper and lower gastrointestinal series are procedures that involve the introduction of a contrast medium known as barium. Barium can be introduced by ingesting or by enema. After induction of the barium, x-rays are taken of the upper and lower gastrointestinal system structures (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, n.d.-g, n.d.-h ). To learn more, visit the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases’ web pages on upper GI series and lower GI series.
The fecal occult blood test is a test for hidden blood in a fecal sample. It can be performed at home and involves the patient putting a small segment of fecal output on a test card that is then mailed to their healthcare provider or a laboratory. Blood detection can be an indicator of bleeding along the digestive tract or an abnormal growth, such as colorectal cancer (MedlinePlus, 2020a).
A stool culture procedure involves the collection of a small sample of feces. The sample is analyzed for abnormal bacterial growth and parasites through a culture check (MedlinePlus, 2020b).
An EGD (upper endoscopy) is a procedure whereby a physician examines the upper gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum) using a special instrument called an endoscope. The physician examines the tissues and is able to take a biopsy, if needed (Ahlawat et al., 2021)
Abdominal
Pertaining to the abdomen.
Abdominoplasty
Surgical repair of the abdomen.
Ampulla
A sac-like enlargement of a canal or duct.
Anal
Pertaining to the anus.
Appendectomy
Excision of the appendix.
Appendicitis
Acute inflammation of the appendix.
Ascites
Abnormal buildup of fluid in the abdomen that may cause swelling.
Bicarbonate
A by-product of the body’s metabolism.
Carbohydrates
Molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates are found in plant-based foods and dairy products and are an important fuel source.
Celiac
Pertaining to the abdomen.
Cholangioma
Tumor of the bile duct.
Cholangiography
Radiographic imaging of the bile duct.
Cholecystectomy
Excision of the gallbladder.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder.
Choledocholithiasis
Condition of gallstones in the common bile duct.
Cholelithiasis
Condition of gallstones.
Cirrhosis
A type of chronic, progressive liver disease in which liver cells are replaced by scar tissue.
Colectomy
Excision of the colon.
Colitis
Inflammation of the colon.
Colonoscope
A thin, tube-like instrument used to examine the inside of the colon.
Colonoscopy
Examination of the inside of the colon using a colonoscope, inserted into the rectum.
Colorectal
Pertaining to the colon or rectum.
Colostomy
An opening into the colon from the outside of the body.
CT colonography
A method to examine the inside of the colon by taking a series of x-rays.
Distal
A position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body.
Diverticulitis
Inflammation of one or more pouches or sacs that bulge out from the wall of a hollow organ, such as the colon.
Diverticulosis
A condition marked by small sacs or pouches in the walls of a hollow organ, such as the colon.
Dysentery
Acute inflammation of the intestine presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea.
Dysphagia
Dyspepsia
Emesis
Emulsification
The process of breaking down the fat into smaller blood cells, which makes it easy for enzymes to function and digest food.
Endoscope
A thin, tube-like instrument used to look at tissues inside the body.
Endoscopy
A procedure that uses an endoscope to examine the inside of the body.
Esophageal
Pertaining to the esophagus.
Esophagitis
Inflammation of the esophagus.
Esophagoscopy
Examination of the esophagus using an esophagoscope.
Exocrine gland
A gland whose secretions leave through a duct that opens directly, or indirectly, to the external environment.
Feces
Semisolid waste product of digestion.
Flatus
Gas in the intestine.
Fundus
The part of a hollow organ that is across from, or farthest away from, the organ’s opening.
Gastrectomy
Gastric
Pertaining to the stomach.
Gastritis
Inflammation of the lining of the stomach.
Gastroenteritis
Inflammation of the lining of the stomach and the intestines.
Gastroenterologist
A doctor who has special training in diagnosing and treating disorders of the digestive system.
Gastroenterology
A subspecialty of internal medicine concerned with the study of the physiology and diseases of the digestive system and related structures.
Gastrojejunostomy
A surgical procedure that connects part of the stomach to the jejunum.
Gastroplasty
Surgical repair of the stomach.
Gastroscope
A thin, tube-like instrument used to examine the inside of the stomach.
Gastroscopy
Examination of the inside of the stomach using a gastroscope passed through the mouth and esophagus.
Gastrostomy
Creation of an artificial opening in the stomach.
Gingivectomy
Excision of the gums.
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums.
Glossitis
Inflammation of the tongue.
Hemorrhoid
An enlarged or swollen blood vessel, usually located near the anus or the rectum.
Hepatitis
Disease of the liver causing inflammation.
Hepatoma
Tumor of the liver.
Hepatomegaly
Herniorrhaphy
Suturing of a hernia.
Ileostomy
A procedure in which the ileum is brought through the abdominal wall.
Labia
Lips of the mouth.
Lacteals
The lymphatic vessels of the small intestine which absorb digested fats.
Laparoscope
A thin, tube-like instrument used to look at tissues and organs inside the abdomen.
Laparoscopy
A procedure that uses a laparoscope, inserted through the abdominal wall, to examine the inside of the abdomen.
Laparotomy
A surgical incision made in the wall of the abdomen.
Lingual tonsil
Lymphoid tissue located at the base of the tongue.
Lymphoid
Referring to lymphocytes or tissue in which lymphocytes develop.
Melena
Black, tarry feces containing blood.
Nasal cavity
The inside of your nose.
Nasogastric
Describes the passage from the nose to the stomach.
Nausea
A feeling of sickness or discomfort in the stomach that may come with an urge to vomit.
Obesity
A common, chronic disease marked by an abnormally high, unhealthy amount of body fat.
Omentum
A fold of the peritoneum (the thin tissue that lines the abdomen) that surrounds the stomach and other organs in the abdomen.
Oral
By or pertaining to the mouth.
Palatine tonsils
A pair of soft tissue masses located at the rear of the throat (pharynx).
Palpation
Examination by pressing on the surface of the body to feel the organs or tissues underneath.
Pancreatic
Pertaining to the pancreas.
Pancreatitis
Inflammation of the pancreas.
Peritoneal
Having to do with the parietal peritoneum (the tissue that lines the abdominal wall and pelvic cavity) and visceral peritoneum (the tissue that covers most of the organs in the abdomen, including the intestines).
Peritonitis
Inflammation of the peritoneum.
Polyp
A growth that protrudes from a mucous membrane.
Polypectomy
Excision of polyps.
Polyposis
The development of numerous polyps.
Proctoscope
A thin, tube-like instrument used to look inside the anus and rectum.
Proctoscopy
A procedure that uses a proctoscope to look inside the anus and rectum.
Proximal
A position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body.
Pyloric sphincter
A band of smooth muscle at the junction between the pylorus of the stomach and the duodenum of the small intestine.
Pyloromyotomy
Incision into the pyloric muscle (used to correct pyloric stenosis).
Rectal
By or pertaining to the rectum.
Rectocele
Herniation of the rectum into the vagina.
Reflux
The backward flow of liquid from the stomach into the esophagus.
Sialolith
Stone in the salivary gland.
Sigmoidoscopy
Examination of the lower colon using a sigmoidoscope, inserted into the rectum.
Steatorrhea
Condition characterized by chronic fatty diarrhea.
Stoma
A surgically-created opening from an area inside the body to the outside.
Stomatitis
Inflammation or irritation of the mucous membranes in the mouth.
Stratified squamous epithelium
Cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane.
Ahlawat, R., Hoilat, G. J., & Ross, A. B. (2021). Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. In StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532268/
Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2021). Physicians and surgeons. In Occupational outlook handbook. U.S. Department of Labor. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/physicians-and-surgeons.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.-a). What is viral hepatitis? https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/abc/index.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.-b). Hepatitis D questions and answers for health professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hdv/hdvfaq.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.-c). Hepatitis E questions and answers for health professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hev/hevfaq.htm
CrashCourse. (2005, September 7). Digestive System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #33 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yIoTRGfcMqM
CrashCourse. (2005, September 22). Digestive System, Part 3: Crash Course A&P #35 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jGme7BRkpuQ
Jones, M. W., Genova, R., & O’Rourke, M. C. (2021). Acute cholecystitis. In StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459171/
Jones, M. W., Gnanapandithan, K., Panneerselvam, D., & Ferguson, T. (2021). Chronic cholecystitis. In StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470236/
MedlinePlus. (2021a). Gerd. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/gerd.html
MedlinePlus. (2021b). Hernia. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/hernia.html
MedlinePlus. (2020a). Fecal occult blood test (FOBT). U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/fecal-occult-blood-test-fobt/
MedlinePlus. (2020b). Bacteria culture test. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/bacteria-culture-test/
National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). Definition of gastroenterologist. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/gastroenterologist
National Cancer Institute. (2021a). Esophageal cancer treatment (adult) (PDQ®)–Patient Version. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.cancer.gov/types/esophageal/patient/esophageal-treatment-pdq
National Cancer Institute. (2021b). Colon cancer treatment (PDDQ®)–Patient Version. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colon-treatment-pdq
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-a). Cirrhosis. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/cirrhosis/all-content
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-b). Celiac disease. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/celiac-disease/all-content
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-c). Crohn’s disease. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/crohns-disease/all-content
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-d). Ulcerative colitis. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/ulcerative-colitis/all-content
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-e). Irritable bowel syndrome. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/irritable-bowel-syndrome/all-content
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-f). Colon polyps. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/colon-polyps/definition-facts
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-g). Upper GI series. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diagnostic-tests/upper-gi-series
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.-h). Lower GI series. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diagnostic-tests/lower-gi-series
TED-Ed. (2014, November 25). What does the liver do? – Emma Bryce [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wbh3SjzydnQ
Figure 13.1 image description: This diagram shows the digestive system of a human being, with the major organs labeled. Labels read (clockwise, from top): salivary glands: parotid gland, sublingual gland, submandibular gland; pharynx, stomach, spleen, pancreas, large intestine: transverse colon, ascending colon, descending colon, cecum, sigmoid colon, appendix, rectum, anal canal, anus; small intestine: duodenum, jejunum, ileum, gallbladder, liver, esophagus, tongue, mouth. [Return to Figure 13.1].
Figure 13.2 image description: This diagram shows an anterior view of the structure of the mouth. The teeth, lips, tongue, gums, and many other parts are labeled. Labels read (clockwise from top): superior lip, superior labial frenulum, gingivae, palatoglossal arch, fauces, palatopharyngeal arch, palatine tonsil, tongue, lingual frenulum, opening duct of the submandibular gland, gingivae, inferior labial frenulum, inferior lip, oral vestibule, incisors, cuspid, premolars, molars, cheek, uvula, soft palate, hard palate. [Return to Figure 13.2].
Figure 13.3 image description: This diagram shows the structures of the tongue and lingual papillae. Labels read (from top): epiglottis, palatopharyngeal arch, palatine tonsil, lingual tonsil, palatoglossal arch, terminal sulcus, foliate papillae, circumvallate papillae, dorsum of the tongue, fungiform papilla, filiform papillae. [Return to Figure 13.3].
Figure 13.4 image description: This diagram shows the esophagus, going from the mouth to the stomach. The upper and the lower esophageal sphincter are labeled. Labels read (from top): upper esophageal sphincter, trachea, esophagus, lower esophageal sphincter, stomach. [Return to Figure 13.4].
Figure 13.5 image description: This image shows a cross-section of the stomach, and the major parts: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus are labeled. Labels read (from top of the stomach): esophagus, muscularis externa (longitudinal layer, circular layer, oblique layer), cardia, fundus, serosa, lesser and greater curvatures, lumen, rugae of mucosa, pyloric antrum, pyloric canal, pyloric sphincter valve at the pylorus, duodenum. [Return to Figure 13.5].
Figure 13.6 image description: This diagram shows the small intestine. The different parts of the small intestine are labeled. Labels read (from top of the small intestine): duodenum, jejunum, ileum, large intestine, rectum. [Return to Figure 13.6].
Figure 13.7 image description: This image shows the large intestine; the major parts of the large intestine are labeled. Labels read (from the start of the large intestinal tract): vermiform complex, cecum, ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, right colic hepatic flexure, left colic splenic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, anal canal. [Return to Figure 13.7].
Figure 13.8 image description: This diagram shows the accessory organs of the digestive system. The liver, spleen, pancreas, gallbladder, and their major parts are shown. Labels read: liver (right lobe, quadrate lobe, left lobe, caudate lobe), spleen, pancreas, pancreatic duct, gallbladder right hepatic duct, cystic duct, common hepatic duct, common bile duct, left hepatic duct. [Return to Figure 13.8].
Figure 13.9 image description: This figure shows the pancreas and its major parts Labels read (from left to right): common bile duct, head of the pancreas, pancreatic duct, lobules, tail of the pancreas. A magnified view of a small region of the pancreas shows the pancreatic islet cells, the acinar cells, exocrine cells, and the pancreatic duct. [Return to Figure 13.9].
Figure 13.10 image description: This figure shows the gallbladder and its major parts are labeled. Labels read (starting in the gallbladder): body, fundus, neck, cystic duct, common hepatic duct, common bile duct, left and right hepatic ducts, liver. [Return to Figure 13.10].
Figure 13.11 image description: This image shows the peristaltic movement of food. In the left image, the food bolus is towards the top of the esophagus and arrows pointing downward show the direction of movement of the peristaltic wave. In the center image, the food bolus and the wave movement are closer to the center of the esophagus and in the right image, the bolus and the wave are close to the bottom end of the esophagus. [Return to Figure 13.11].
Figure 13.12 image description: This image shows the different processes involved in digestion. The image shows how food travels from the mouth through the major organs. Associated textboxes list the various digestive processes: Absorption (nutrients and water to blood vessels and lymph vessels (small intestine), water to blood vessels (large intestine)), propulsion (swallowing (oropharynx), peristalsis (esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine), chemical digestion, mechanical digestion (chewing (mouth), churning (stomach), segmentation (small intestine)). Parts of the digestive tract are labeled: ingestion of food, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, feces, anus, defecation. [Return to Figure 13.12].
Unless otherwise indicated, this chapter contains material adapted from Anatomy and Physiology (on OpenStax), by Betts et al. and is used under a CC BY 4.0 international license. Download and access this book for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.
definitionLips; can refer to the lips of the mouth or the folds of hair-covered skin that begin just posterior to the mons pubis (Betts et al., 2013)